What is Project Management?
ByJulian Gette
Workast publisher
Workast publisher
Project management is a critical process for achieving successful outcomes in any project, whether it's launching a new product, constructing a building, or planning an event. In this guide, we'll define project management, discuss its importance, and explore the different types of project management styles.
Project management is the process of planning, executing, and monitoring the progress of a project to achieve its objectives within a specified time frame and budget. It involves managing resources, tasks, timelines, and risks to ensure that the project is completed successfully.
Effective project management is critical for achieving project success. It enables teams to work together more efficiently and effectively, reduces the risk of project failure, and ensures that projects are completed on time and within budget. Project management also helps organizations to:
Align project goals with organizational goals
Plan and prioritize projects
Manage resources effectively
Identify and mitigate project risks
Monitor project progress and performance
Communicate with stakeholders
Adapt to changes and unforeseen events
There are various project management styles, each with its own unique approach and methodology. Here are the most common types of project management styles:
Waterfall Project Management
Waterfall project management is a linear, sequential approach to project management, where each phase of the project is completed before moving on to the next phase. The project phases typically include requirements gathering, design, development, testing, and deployment. This style is best suited for projects with well-defined objectives, scope, and timelines.
Agile Project Management
Agile project management is an iterative approach to project management, where the project is broken down into smaller, more manageable parts, called sprints. Each sprint involves planning, execution, and review, allowing for continuous feedback and improvement throughout the project. Agile project management is best suited for projects that require flexibility, collaboration, and adaptability.
Scrum Project Management
Scrum project management is a subset of agile project management, where the project is broken down into short, time-boxed sprints, and the team works collaboratively to deliver a working product at the end of each sprint. The process involves daily stand-up meetings, sprint planning, sprint reviews, and retrospectives.
Lean Project Management
Lean project management is a methodology that focuses on reducing waste, maximizing efficiency, and delivering value to customers. It involves continuous improvement, eliminating non-value-added activities, and optimizing processes. Lean project management is best suited for projects with a focus on delivering high-quality products or services quickly and efficiently.
Six Sigma Project Management
Six Sigma project management is a data-driven methodology that focuses on reducing defects and errors in processes, products, and services. It involves identifying and eliminating root causes of defects, measuring and analyzing data, and implementing improvements to reduce variability and improve quality. Six Sigma project management is best suited for projects that require a high degree of precision and quality control.
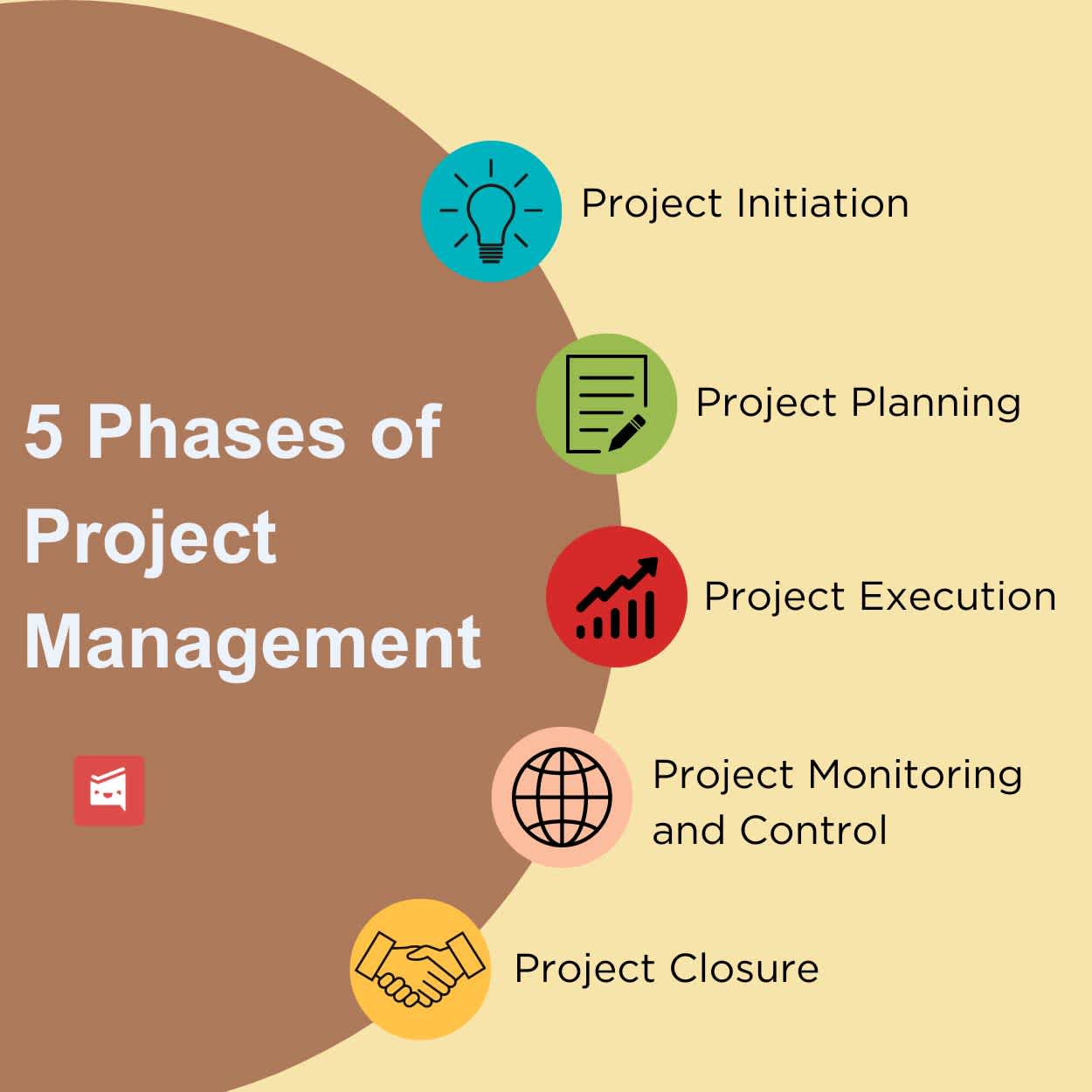
1. Project Initiation: This is the first phase of project management where the project is defined, and the project goals, objectives, and scope are identified. The project team is also assembled during this phase, and the project manager is assigned. The project manager then creates a project charter, which outlines the scope, goals, and objectives of the project.
2. Project Planning: This phase involves creating a project plan, which outlines the steps needed to achieve the project goals and objectives. The project plan includes the project schedule, budget, resource allocation, risk management plan, and communication plan. The project manager may also create a work breakdown structure (WBS), which breaks down the project into smaller, more manageable tasks.
3. Project Execution: This phase involves executing the project plan, and it is where the project team works to complete the project tasks. The project manager monitors the project's progress, and the project team collaborates to address any issues that arise during the project. The project manager may also need to adjust the project plan if any changes are needed.
4. Project Monitoring and Control: This phase involves monitoring the project's progress and making sure that it stays on track. The project manager reviews the project's performance against the project plan, and they take corrective actions to keep the project on track. They also monitor the project's budget, scope, and schedule and make adjustments as necessary.
5. Project Closure: This phase involves wrapping up the project and ensuring that all deliverables are complete. The project team conducts a final review to ensure that the project goals and objectives have been achieved. The project manager also creates a final report, which documents the project's success and any lessons learned during the project. Finally, the project manager hands over the project deliverables to the stakeholders and closes out the project.
Project management is a critical process that is applicable to almost any industry or field that involves completing projects. Here are some examples of industries where project management is commonly used:
- Construction: Project management is commonly used in construction projects, where project managers are responsible for ensuring that projects are completed on time and within budget.
- Information Technology: Project management is used in software development, system implementation, and other IT-related projects.
- Healthcare: Project management is used in healthcare to manage projects related to improving patient care, implementing new healthcare technologies, and managing healthcare facilities.
- Marketing and Advertising: Project management is used in marketing and advertising to manage campaigns, product launches, and other initiatives.
- Education: Project management is used in education to manage projects related to curriculum development, school building construction, and other educational initiatives.
- Engineering: Project management is used in engineering to manage projects related to the design and construction of buildings, bridges, and other infrastructure projects.
- Manufacturing: Project management is used in manufacturing to manage projects related to the design, development, and production of products.
- Government: Project management is used in government to manage projects related to infrastructure development, public safety initiatives, and other public projects.
Project management is a versatile process that can be applied to almost any industry or field where projects need to be completed. By using effective project management techniques, businesses and organizations can improve project efficiency, reduce the risk of project failure, and ensure that projects are completed on time and within budget. Project management is a critical process for achieving successful outcomes in any project. By understanding the different project management styles and selecting the right one for your project, you can improve project efficiency, reduce the risk of project failure, and ensure that projects are completed on time and within budget. Whether you choose a waterfall, agile, scrum, lean, or Six Sigma approach, the key is to select a methodology that aligns with your project goals and objectives